Archive
Carménère – Lost, Found, Evolved, Delightful
 According to the 2012 edition of the famous Wine Grapes book (written by Jancis Robinson, Julia Harding, and Dr. José Vouillamoz), there are 1368 grapes used in winemaking. It would be a safe bet to say that each one of those grapes has its own story. Of course, not all of those stories would be dramatic and exciting, but I’m sure some would read as a good detective story, probably without much of the shootouts.
According to the 2012 edition of the famous Wine Grapes book (written by Jancis Robinson, Julia Harding, and Dr. José Vouillamoz), there are 1368 grapes used in winemaking. It would be a safe bet to say that each one of those grapes has its own story. Of course, not all of those stories would be dramatic and exciting, but I’m sure some would read as a good detective story, probably without much of the shootouts.
Carménère is a perfect candidate for such a story. When Bordeaux ruled the wine world – which would be in the middle of 1800th – Carménère (which translates from French as crimson, identifying a beautiful color of the grapes) was one of the “big six” Bordeaux varieties, comprising all of the Bordeaux wines – Cabernet Sauvignon, Cabernet Franc, Merlot, Malbec, Petite Verdot, and Carménère. Carménère is related to Cabernet grapes, but historically it is not very clear if Carménère was some type of clone of Cabernet, or if it was the other way around.
The phylloxera epidemic of 1867 put a damper on all the wine production in France and forced vignerons to replant all of the vines on the Phylloxera-resistant rootstock. Carménère is not an easy grape to grow in the Bordeaux climate, and it was pretty much abandoned and considered extinct at the beginning of the 20th century.
Meanwhile, in 1850th, immigrants brought many of the French grapes with them to Chile, where the grapes started to strive in the warm and dry climate offered by the Andes mountains. In 1980th, Merlot became a star of Chilean winemaking, abundantly producing inexpensive wines that became well known in the world. It was noticed that the taste of the Chilean Merlot differs from the traditional Merlot and that Merlot was considered to be a Chilean-specific clone. Or at least it was until 1994 when visiting French scientist, Jean Boursiquot noticed that Chilean Merlot has different leaves and grape clusters from the traditional Merlot, and was able to show that this was not the Merlot, but long-extinct Carménère, which successfully made it to Chile in the 1850s with all the Bordeaux grape cuttings.
From that time, Carménère went on to become Chile’s own star grape, and answer to another French variety, Malbec, which Argentina made its own. As Phylloxera never made it to Chile, Chilean Carménère was even brought back to France, but it is not an easy grape to deal with, so it never regained its past glory in Bordeaux.
TerraNoble winery (Terra Noble means “Noble Land”), was founded in 1993 by a group of friends. From the beginning, TerraNoble focus was on producing high-end wines in Maule Valley, and the winery quickly established itself as a boutique producer of Chilean Merlot. After Chilean Merlot was identified as Carménère, TerraNoble continued focusing on the variety.
TerraNoble sustainably (certified sustainable since 2019) farms today about 750 acres, which comprises 4 vineyards in Maule Valley, Colchagua Valley, and Casablanca Valley. The winery produces a full range of wines you would expect a Chilean winery to produce – Chardonnay, Sauvignon Blanc, Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, Syrah – but Carménère is unquestionably the darling of TerraNoble, as presented by Marcelo Garcia, TerraNoble’s winemaker, during the virtual tasting a few weeks back.
While browsing Sotheby’s New Wine Encyclopedia by Tom Stevenson, I came across a small insert about Chilean Carménère, where it was mentioned that Carménère is site-specific to the extreme – you need to work hard to find the right location for Carménère to vines to deliver the best result. TerraNoble approach to Carménère is based exactly on this notion – site-specific Carménère wines. As we mentioned before, Carménère is a close relative of the core Bordeaux varieties – Cabernet and Merlot and has a similar taste profile as well. It is similar, but not the same, obviously. A typical Carménère has a much higher concentration of the aroma compound called pyrazines, which is often associated with the pronounced taste of the green bell pepper – here is a good article that explains pyrazines in depth. Green pepper is good for cooking and the salad, but probably not so much in wine. Also, when left unsupervised, Carménère has a tendency to develop a high concentration of the tannins. While someone might enjoy a big powerful wine with pronounced green bell pepper aromatics and powerful tannin structure, the appeal is not universal and this is what Chilean winemakers had to deal with.
In 1998, TerraNoble released Gran Reserva Carménère to the international markets. The grapes for this wine were coming from the La Higuera Vineyard in Maule Valley, near San Clemente. This wine still remains the winery’s flagship. I had been a fan of TerraNoble wines for a long time, after discovering them back in 2004. To the best of my memory, 2003 TerraNoble Carménère Gran Reserva was quite enjoyable, but I don’t have any detailed notes in that regard.
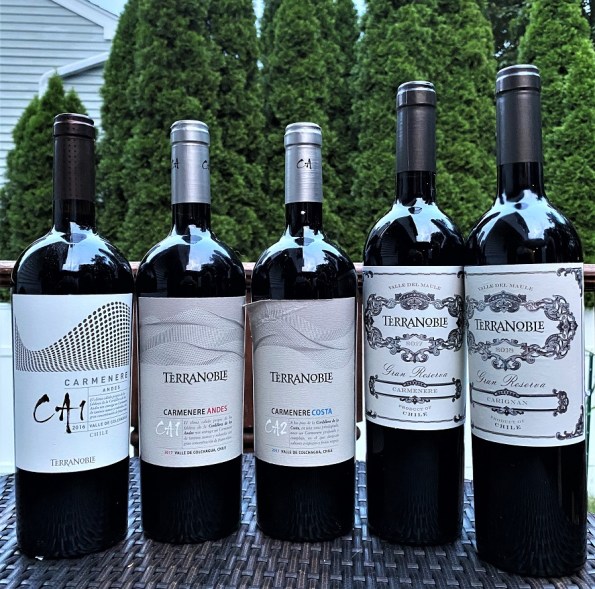
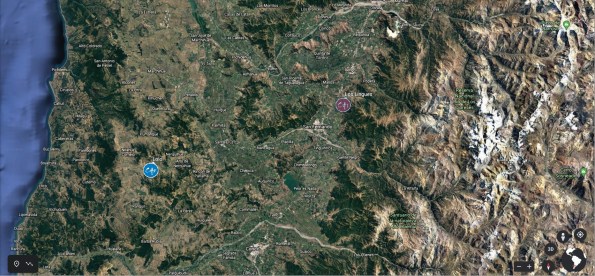
Following its Carménère calling, TerraNoble planted two new Carménère vineyards in Colchagua Valley – in 2004, Los Cactus Vineyard, about 25 miles from the coast, and in 2005, Los Lingues Vineyard, about 35 miles further inland, on the outskirts of Andes mountains. These two vineyards became a home to the special project called CA – producing two 100% Carménère wines using absolutely identical vinification at the winery, different only in the source of the grapes – CA1 from the Andes, and CA2 from the coast. The first wines in the CA project were released in 2009.
The goal of the project was to showcase the capabilities of Carménère grapes. With winemaking techniques identical for both wines, different taste profiles were only influenced by the different growing conditions, the terroir – soil and climate most of anything. How different are the wines? We had an opportunity to taste a few of the CA project wines, and they were demonstrably different. Here are my notes from the tasting.
We started with the tasting of the flagship Carménère
2017 TerraNoble Carmenere Gran Reserva Maule Valley, Chile (14% ABV, $18.99, aged 75% in previously used French oak barrels, 25% in untoasted casks, 6 months in the bottle)
Dark garnet
Currant leaves, blackberries
Bright red fruit, good acidity, soft, easy to drink, medium body, medium finish.
8-, nicely approachable from the get-go. 8 after a few hours.
Then we had an opportunity to compare two of the vintages of CA1 wines (from the Andes), and then CA1 and CA2 from the same vintage – again, you can see how different the wines are:
2016 TerraNoble CA1 Carmenere Andes Valle de Colchagua, Chile (14% ABV, $24.99, aged 85% in new and twice used French oak barrels, 15% in untoasted oak casks for 14 months, 12 months in the bottle)
dark garnet
touch of barnyard, dark fruit
black currant, a touch of bell peppers, noticeable french oak tannins, peppery, chewy tannins, big body
7+/8- initially, 8 after a few hours. Excellent, powerful wine.
2017 TerraNoble CA1 Carmenere Andes Valle de Colchagua, Chile (14% ABV, $24.99, aged 85% in new and twice used French oak barrels, 15% in untoasted oak casks for 14 months, 12 months in the bottle)
dark garnet
tobacco, currant leaves, pepper, dense and concentrated
good acidity, peppery notes, blackberries, concentrated
7+/8- initially, 8 in a few hours. Delicious.
2017 TerraNoble CA2 Carmenere Costa Valle de Colchagua, Chile (14% ABV, $24.99 aged 85% in new and twice used French oak barrels, 15% in untoasted oak casks for 14 months, 12 months in the bottle)
dark garnet
currant more noticeable
softer than the previous wine, but showing more of the green notes. black currant
7+/8- initially, 8 in a few hours.
 We finished our tasting with a somewhat unexpected wine – Carignan. Carignan is another ancient French grape, this one coming from Rhône valley. Chile has very old Carignan vineyards (some are 120+ years old), however, for the longest time, Carignan was used by the farmers to make very strong, but not really drinkable alcohol. Carignan’s popularity started increasing around 2000. Another interesting fact about Carignan is that it is mostly growing in the small (and old) vineyards, where the vineyards became a part of a natural biodiverse habitat, which includes other plants and animals.
We finished our tasting with a somewhat unexpected wine – Carignan. Carignan is another ancient French grape, this one coming from Rhône valley. Chile has very old Carignan vineyards (some are 120+ years old), however, for the longest time, Carignan was used by the farmers to make very strong, but not really drinkable alcohol. Carignan’s popularity started increasing around 2000. Another interesting fact about Carignan is that it is mostly growing in the small (and old) vineyards, where the vineyards became a part of a natural biodiverse habitat, which includes other plants and animals.
TerraNoble Carignan grapes were sourced from the vineyard planted in 1958 in Maule Valley close to the ocean, using dry farming. The wine was partially aged in the concrete eggs.
2018 TerraNoble Carignan Gran Reserva Melozal, Maule Valley, Chile (13.5% ABV, $18.99, aged 50% in concrete egg, 50% in untoasted oak casks, 6 months in the bottle)
Dark Ruby
touch of licorice, distant hint of candied fruit
tart fresh cherries, good acidity, medium body, simple, easy, and pleasant. Might be a summer quaffer
7+
Here you are, my friends – TerraNoble tells the story of modern-day Chilean Carménère. The evolution of the Carménère wines is still ongoing, with TerraNoble winemakers starting to experiment with concrete eggs and amphorae, and who knows what else is coming to push the grape which Chile made its own even further. One thing for sure – winelovers are in for lots of pleasure.
Wednesday’s Meritage – Wine Quiz Answer, #MWWC5 Vote, Peter Mondavi Turns 99, The Oldest Wine Cellar?, and more
Meritage time!
First, let’s start with the answer for the wine quiz #83, grape trivia – Carménère.
In the quiz, you were supposed to answer 5 questions about red grape called Carménère. Here are the questions, now with the answers:
Q1: Explain the name of the grape Carménère
A1: The name Carménère originates from the French word for crimson, carmin – that relates to the fact that the leaves of Carménère turn beautiful crimson color in the fall.
Q2:Similar to Merlot/Carménère confusion in Chile, the discovery was recently made in one of the well known old world wine producing countries – the grape they thought was ___, actually happened to be a Carménère. Name the grape, the country, and the region within this country where confusion took place.
A2: For the long time, winemakers in Friuli-Venezia Giulia in Italy thought that they were making the wines from Cabernet Franc – only to find out that it was actually a Carménère!
Q3: As the sequel to the previous question – the confusion also spread into the New Wolrd winemaking country. Name the grape been mistaken and the country.
A3: New Zealand imported Cabernet Franc vines out of all places, from Italy – oops? Yes, It was actually a Carménère!
Q4: Wine Spectator calls wines rated in 95-100 range Classic (the highest and the most prestigious category). True or False: there are no Carménère-based wines rated in the Classic category
A4: False . A number of Chilean wines from Casa Lapostolle got the 96 rating, and they are a Carménère-based blends
Q5: Name three grapes, often blended together with Carménère.
A5: Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot and Cabernet Franc are often blended together with Carménère.
“We had rather a low participation in the quiz, but – we do have a winner” – was my opening line here. Now, with the last second entry, we have two winners! Patty from P’s 2013 photo project and Namie from Eat with Namie both correctly answered all 5 questions, and they both get the prize of unlimited bragging rights. Well done!
Now, to the interesting stuff around the vine and the web!
I have a few interesting things for you. First, you can vote now for the winner of the Monthly Wine Writing Challenge #5, with the theme called “Feast”. Here is the link to the blog post where you will find all the contenders’ blog posts and can vote!
The next article I want to bring to your attention is from the Wine Spectator, and it is dedicated to the Peter Mondavi – the older brother of Robert Mondavi. As amazing as it sounds, Peter Mondavi turns 99, and he still actively runs his winery, Charles Krug in Napa Valley. You can find the article here – definitely an interesting read, very relevant to the past and present of California wine.
How old do you think the oldest known wine cellar is and where do you think it is located? An archaelogical excavation in the norther Israel unearthed a cellar, which is estimated to be 3,700 years old. I think this is a very respectful age. No, the wine didn’t survive for that long, but nevertheless, I think this is a fascinating find. Here is the link for the Wall Street Journal article with more details.
Thanksgiving, an American holiday we will celebrate on Thursday, prompts lots of conversations about wine, and American wine in particular. I want to bring to your attention a very interesting article written by Mike Veseth at The Wine Economist blog, where he is talking about American wines. When we say “American Wines”, we actually don’t mean the wines made only in California – the wines are produced in all 50 states, and 12 of those states have more than a 100 wineries each! I find this information very interesting. Also from Mike’s article you can jump to the web site called Wines and Vines, which seems to offer a wealth of data regarding the wine industry – check it out.
Last but no least – don’t forget WTSO Gift Marathon on December 2nd (full details can be found here). WTSO just announced some of the wines which will be a part of the marathon – Beringer, Insignia, Philippe Prie, Caymus – I think it will be a very interesting event, so point your browser to the WTSO on Monday, December 2nd and happy hunting!
Ahh, and before we part – Happy Thanksgiving and Happy Hanukkah!
That’s all I have for you for today, folks. The glass is empty – but refill is on its way. Until the next time – cheers!
Weekly Wine Quiz #83: Grape Trivia – Carménère
The Wine Quiz series is not meant to intimidate. The whole idea here is to have fun and learn something new. When answering the questions, it is fully encouraged to use all available sources of information, including Google or any other search engine. There are no embarrassing answers – the most embarrassing thing is not giving it a try…
Welcome to your new wine quiz!
We are continuing our grape trivia series, with the focus again on the red grapes, and today’s subject is Carménère.
Let’s start with pre-quiz before the quiz. Class, how many of you heard of the Carménère grape, raise your hands. Ok, now, how many of you tasted the Carménère wines, raise your hands. Okay, those of you who raised their hand twice, can probably skip directly to the main quiz, and for the rest of us, lets talk about Carménère.
When it comes to the Bordeaux, everybody knows five main grapes – Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, Cabernet Franc, Malbec and Petit Verdot. Truth of the matter is that it is actually six – and Carménère is that grape number six. Until the Phylloxera epidemic of the 1870s in France, Carménère was probably one of the leading grapes in Bordeaux. Carménère is related to the Cabernet family, it most likely predates both Cabernet Franc and Cabernet Sauvignon, and it was probably the driving force behind power and finesse of Claret of the 1800s and even before. However, Carménère is a difficult grape to work with – it ripens two to three weeks later than Merlot, and it is susceptible to the viticultural hazard called coulure – the condition when in the cold spring the buds will fail to turn into the flowers. It also doesn’t graft on the new rootstock very easily. So the combination these issues lead to the situation that after the Phylloxera epidemic, the grape was practically not replanted back in Bordeaux, and it was literally considered extinct (it exists today in France, but in the extremely low quantities).
During the 1850s, a lot of Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot cuttings made it to Chile – both in legal and probably illegal ways. For the long time, Chilean winemakers were wondering, why some of their Merlot plantings ripen so late compare to the others, and have a different flavor profile – those grapes where considered to be a specific Chilean Merlot clone. Until in 1994 it was discovered that Chilean Merlot is actually a … Carménère! Carménère made it to Chile in 1850s as part of those Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot cuttings, and it happened to strive in the warm and dry climate. Today, Chile has almost 9,000 hectares planted with Carménère, and it is widely considered one of the best wines Chile can produce.
When ripen properly, Carménère produces excellent powerful wines with the fruit profile somewhat similar to Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot, but with very present herbal and spicy component of sage, pepper, eucalyptus and even menthol.
And now, to the quiz!
Q1: Explain the name of the grape Carménère
Q2:Similar to Merlot/Carménère confusion in Chile, the discovery was recently made in one of the well known old world wine producing countries – the grape they thought was ___, actually happened to be a Carménère. Name the grape, the country, and the region within this country where confusion took place.
Q3: As the sequel to the previous question – the confusion also spread into the New Wolrd winemaking country. Name the grape been mistaken and the country.
Q4: Wine Spectator calls wines rated in 95-100 range Classic (the highest and the most prestigious category). True or False: there are no Carménère-based wines rated in the Classic category
Q5: Name three grapes, often blended together with Carménère.
Good luck, enjoy the quiz and your weekend! Cheers!